Values analysis is the first step to advance the efficiency of your management plan. This topic introduces the values there are in heritage management.
The Steps
First, ask yourself who values your heritage and why.
Then you need to find the relationship between those values and the heritage’s essence.
What are the values’ meaning and importance? Are other objects related to your heritage and do the play a role in those values?
What impact does the context of the heritage have?
Does other heritage share similar values? Are they comparable or related to your heritage?
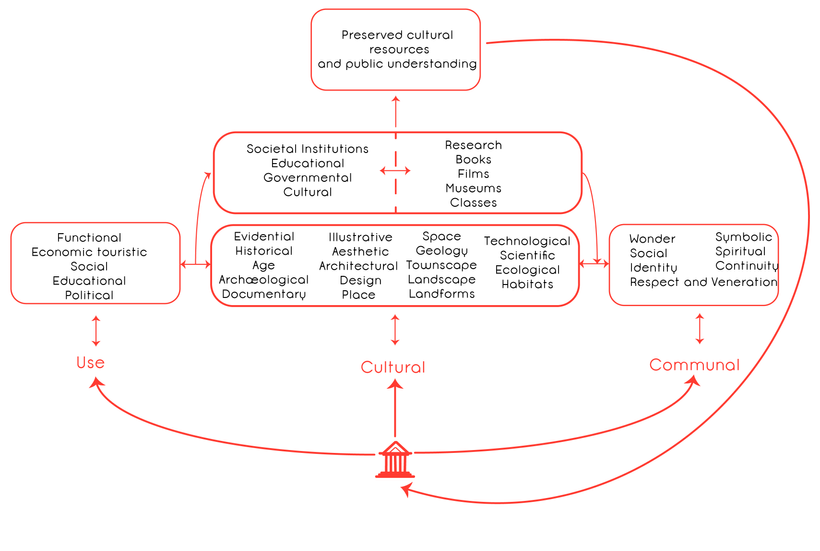
Values
Here is our grouping of values, based on the existing literature and making a compilation. Some are presented differently by other cultural heritage institutions, to showcase them in a clear and appropriate to the context manner.
Cultural Values
- Evidential value: does the heritage provide information about the human activity?
- Historical value: how does the heritage connect the past to the present? (These can be events, people, lifestyle)
- Documentary value: does the heritage provide information about human life?
- Age: determines the age of heritage, and ties it to a specific an era in human history.
- Archaeological: holds archaeological evidence.
- Illustrative value: tied to historic value, the heritage can help interpret the past and form associations with people, art, way of life.
- Aesthetic: how people view and intellectually appreciate the heritage. Such as the architectural design, beauty and harmony.
- Architectural: can have a unique architectural design or be part of a movement.
- Design: features elements of its design (architectural, structural, engineering,etc.)
- Geology: the grounds of a heritage place.
- Townscape: the urban appearance of a town or city is distinct.
- Landscape: the heritage is part of a distinctive landscape.
- Landforms
- Place: heritage site is an important place.
- Space: the space in an around heritage holds importance, and is not necessarily a fixed landscape but can be moveable.
- Ecological: holds a notable combination of plant and animal life.
- Habitats
- Technological scientific: represents significant achievements in these fields.
Communal Values/Emotional Values
People relate and attribute to meaning to heritage. Emotional values add symbolic aspects to “historic” and “aesthetic values”, give meaning” to people, form their identity and an emotional bond with heritage.
- Wonder
- Social: social interaction and connection with other people.
- Identity: provides a sense of identity.
- Symbolic: attributes meaning.
- Spiritual: beliefs and part of organised religion, spirit, understanding, enlightenment, insight.
- Respect and Veneration
- Continuity: do the emotional values have meaning to people today?
Use values
Use values refer to the continuity of communal values and the aspects of the promotion of a heritage today.
- Functional
- Economic and touristic
- Social
- Educational
- Political
The recognition of values expanded from the work of Aloïs Riegl at the beginning of the 20th century and continue today. The ICOMOS charters inform the subject regularly.
I want to learn more:
ICOMOS International Council on Monuments and Sites
Principles for the recording of monuments, groups of buildings and sites (1996)
The Australia ICOMOS Charter for the Conservation of Places of Cultural Significance (The Burra Charter) (1981, updated in 2013)
Document on historic urban public parks – (2017)
Industrial Heritage The International Committee for the Conservation of the Industrial Heritage
International Conference on Conservation
“Cultural Heritage as the Foundation of the Development of Civilisation” (2000)
The Getty Conservation Institute, Los Angeles
“Values and Heritage Conservation Research Report”
English Heritage’s publication “Conservation principles policies and guidance for the sustainable management of the historic environment” is a handy guide to this topic.
Note: as a heritage item has a multidimensional definition, we will refer to a heritage place/object/document/intangible etc. as heritage.

