The historical journey of art conservation and restoration spans epochs, beginning with ancient civilizations acknowledging the intrinsic value of cultural artefacts. From the spiritual dimensions of ancient Egypt to the meticulous preservation efforts in ancient Greece, civilizations recognized the symbolic importance of artworks, emphasizing meticulous preservation.
©VENIS STUDIOS
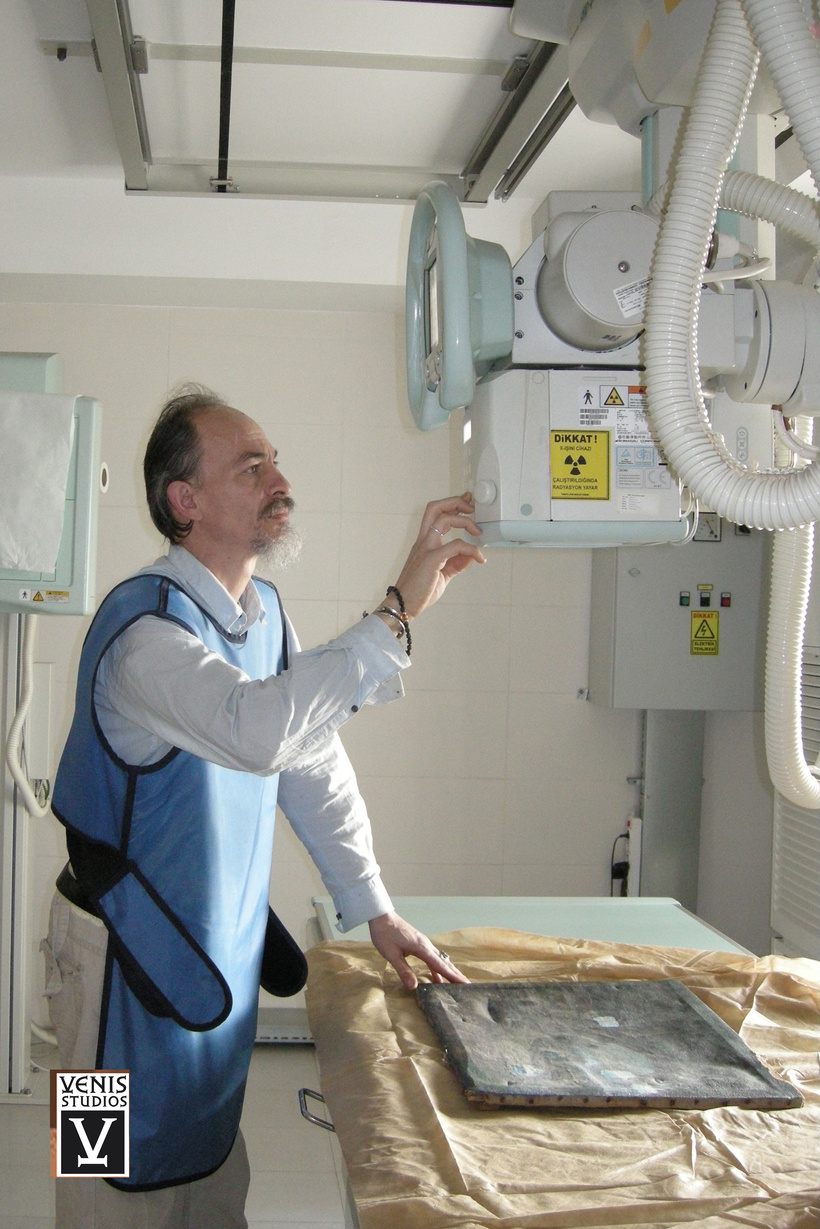
As civilizations progressed, so did conservation methods. Greco-Roman societies and medieval religious institutions contributed to preserving sculptures and manuscripts. The Renaissance marked renewed emphasis, though restoration efforts remained surface-level. The 19th century saw organized conservation efforts, evolving into a professionalized discipline in the 20th century with cutting-edge technologies and a shift toward scientific research and ethical considerations.

©VENIS STUDIOS
Art Conservation and Restoration: A Marriage of Art and Science:
In the 20th century, art conservation embraced a professionalized discipline, uniting artistic intuition with scientific rigour. Ethical considerations, exemplified by the Venice Charter, emphasize cultural heritage authenticity. The expertise required for conservation necessitates seasoned professionals, balancing authenticity and contemporary aesthetic expectations.

©VENIS STUDIOS
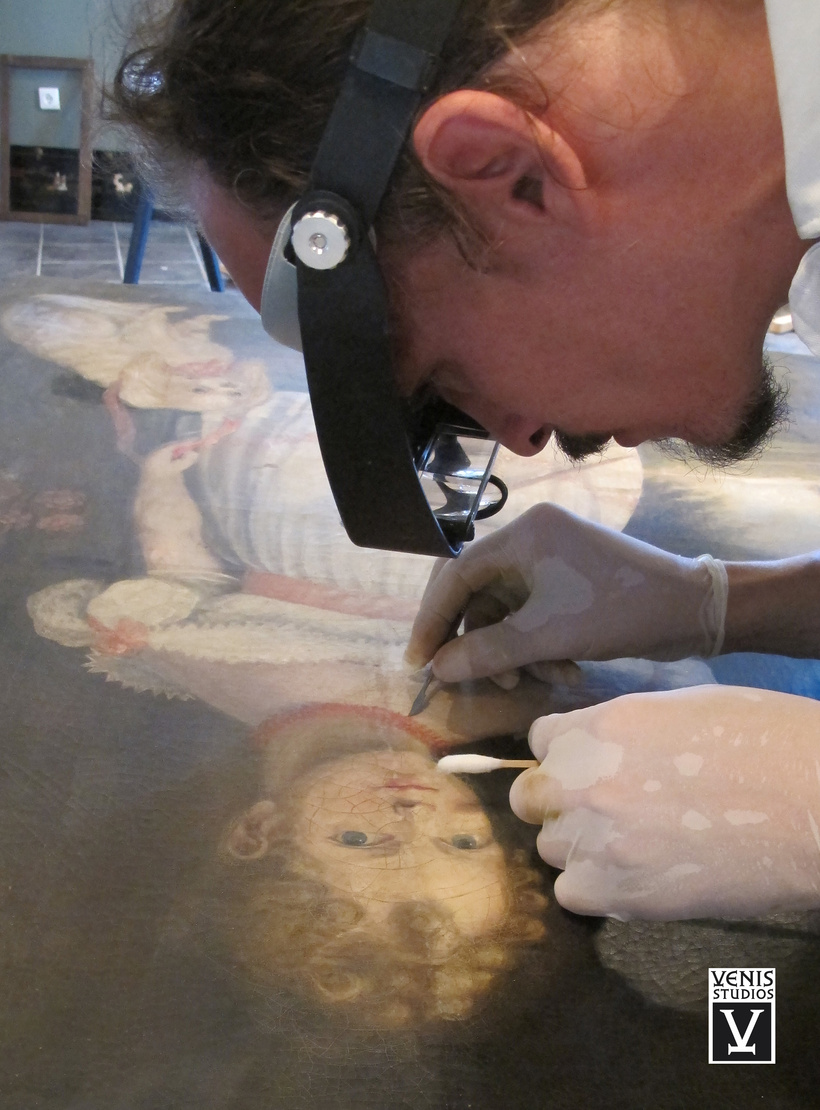
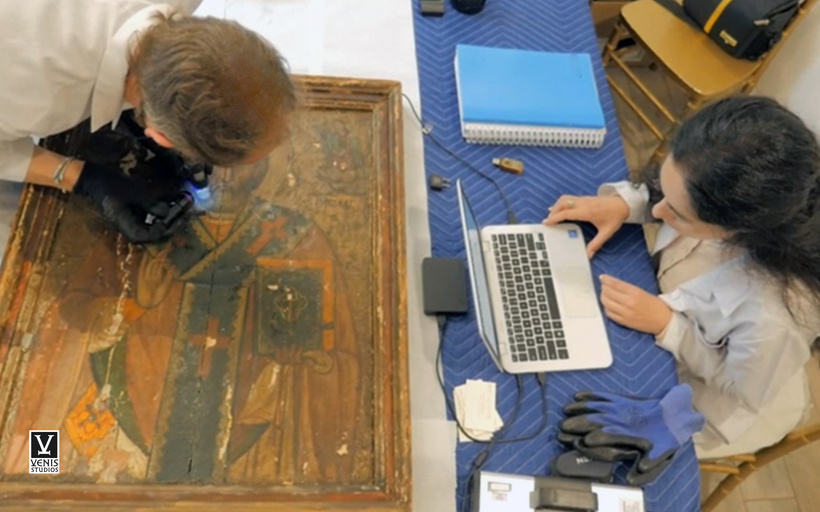
What is Art Conservation and Restoration?
Art conservation and restoration are disciplines preserving historic artworks, ensuring authenticity, originality, and longevity. Conservation focuses on the preservation of authentic artworks, while restoration meticulously repairs damage with respect for historical authenticity and originality.
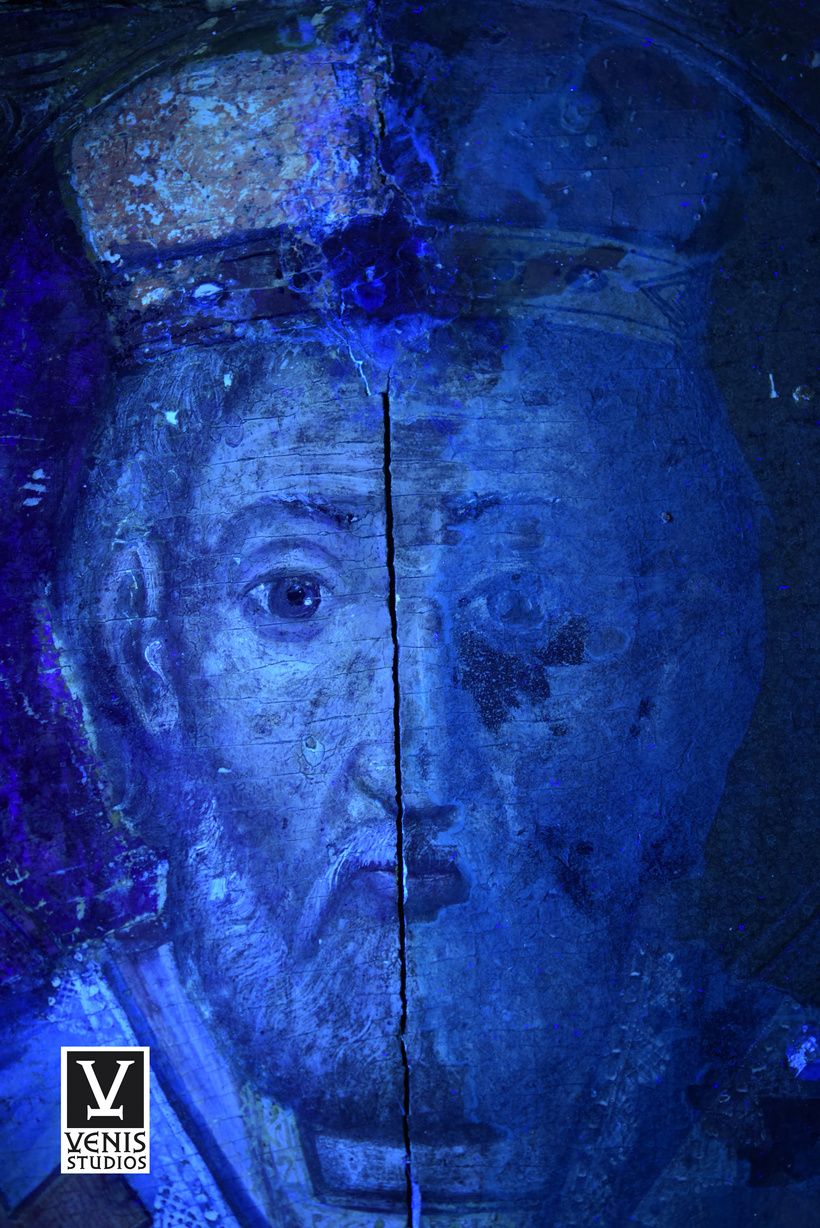
Difference between Making Art and Art Conservation and Restoration:
Making art involves original creation, while conservation and restoration preserve existing artworks. Only professional art conservators and restorers, with a deep understanding of both art and science, can handle the complexities involved.

©VENIS STUDIOS
Limits of Forgery in Art Conservation and Restoration:
Forgery contradicts the principles of conservation, intentionally creating false imitations and destroying authenticity. Ethical considerations, historical integrity, and transparency in documentation are crucial. In essence, forgery undermines the commitment to truthfully preserving and restoring artworks.
Preserve, Conserve, Restore: Ensuring Cultural Heritage’s Truthful Legacy:
Expert professional art conservators and restorers, armed with artistic and scientific knowledge, play a pivotal role in preserving our historic cultural heritage. By conserving and restoring, we understand our past, learn from history, and ensure a strong, truthful future for humanity.
I want to learn more:
by Venizelos G. Gavrilakis
Edited Athina Gkouma
About the author:
Venizelos G. Gavrilakis, a renowned expert in the art conservation and restoration of Byzantine and post-Byzantine icons, historical oil paintings, and Ottoman-era artwork, has been working as a senior expert conservator and restorer since 1994. He has worked with various institutions and has been involved in international conservation meetings and conferences. Gavrilakis is the president of the art conservation and restoration company VENIS STUDIOS, based in Istanbul, Turkey, and has collaborated with galleries, antique dealers, and private collectors.
- Academia
- Articles: World Art News articles
- Interview: Preserving The Past, Embracing The Future: An Interview With Venizelos Gavrilakis, President Of Venis Studios
Our related articles

